Click Here to Visit our Oregon Hemp Farm
The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system consists of receptors, (endogenous cannabinoids or "endocannabinoids"), and enzymes.
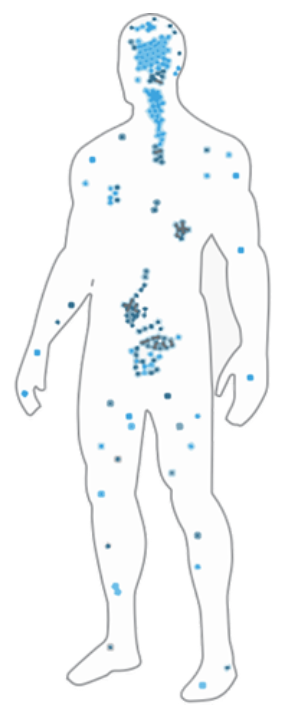
Endocannabinoid Receptors are located all over the body – organs, connective tissues, glands, immune cells, etc.
The Endocannabinoid System includes two primary types of receptors that bind with cannabinoids: CB1 and CB2.
While THC fits directly into the CB1 receptor, cannabidiol does not fit into either type of receptor perfectly. Instead, it stimulates activity in both receptors. This results in changes within any cells that contain either receptor. Because CB1 and CB2 receptors are present throughout the body, the effects of CBD are considered systemic.
"Endocannabinoids are arguably one of the most widespread and versatile signaling molecules known to man."
University of California, L.A., Health Sciences Statement on CBD
Receptors are large, complex molecules (usually proteins) that are in the cell wall. Certain substances can react with these receptors. Like a key opening a lock: if the substance matches the complex structure of the receptor, a reaction may be initiated. The receptor changes its structure, which activates a process within the cell. Some substances bind to the receptor without causing a reaction and block the effect. These are antagonists. An agonist is a substance that activates the receptors and ensures that the normal process is initiated.
The World Health Organization has published the most comprehensive summation of CBD and its studied and published effects. Click here to the CANNABIDIOL (CBD), Pre-Review Report Agenda Item 5.2, Expert Committee on Drug Dependence, Thirty-ninth Meeting Geneva, 6-10 November 2017.
/bendland/images/LocalSalsa-TypeOnlyOneLine-01-d50dc.jpg)
Product Launch Envisioneering